leapfrog#
Proceed state of engine by the leapfrog method.
Description and Assumptions
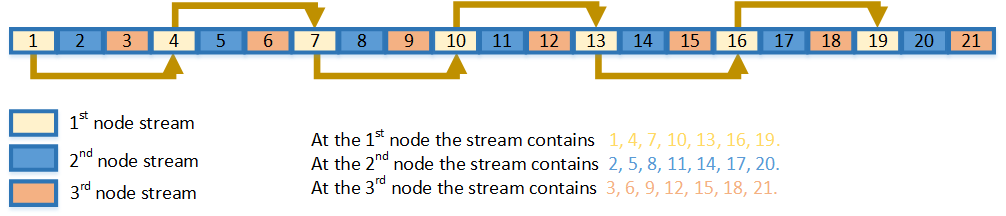
oneapi::math::rng::leapfrog function generates random numbers in an engine with non-unit stride. This feature is particularly useful in distributing random numbers from the original stream across the stride buffers without generating the original random sequence with subsequent manual distribution. see Figure “Leapfrog Method”.
Leapfrog Method
leapfrog#
Syntax
namespace oneapi::math::rng {
template<typename EngineType>
void leapfrog(EngineType& engine, std::uint64_t idx, std::uint64_t stride);
}
Template Parameters
- EngineType
Type of engine. Note: may not be supported by all available engine classes.
Input Parameters
- engine
Engine which state would be skipped.
- idx
Index of the computational node.
- stride
Largest number of computational nodes, or stride.
Example
// Creating 3 identical engines
oneapi::math::rng::mcg31m1 engine_1(queue, seed);
oneapi::math::rng::mcg31m1 engine_2(engine_1);
oneapi::math::rng::mcg31m1 engine_3(engine_1);
// Leapfrogging the states of engines
oneapi::math::rng::leapfrog(engine_1, 0 , 3);
oneapi::math::rng::leapfrog(engine_2, 1 , 3);
oneapi::math::rng::leapfrog(engine_3, 2 , 3);
// Generating random numbers
Parent topic: Host Service Routines
